The pons (in green) are a part of the brainstem, located superior (that is to say, above) to the medulla. It serves as a connector between the cerebrum and the cerebellum. In fact, “pons” is the Latin word meaning bridge. Damage to the pons could possibly lead to loss of all muscle functions except eye movements. While it may look relatively small compared to the rest of the brain, the pons are just as important as any other brain structure.
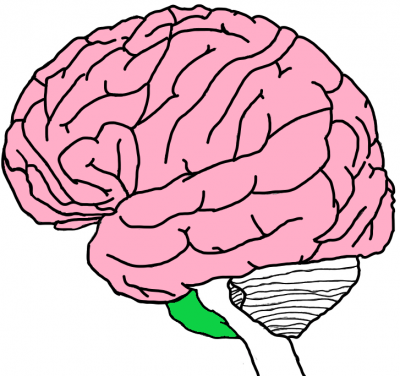
The main structures in the pons are listed and described below.
- The ventral pons: These contain the pontine nuclei, which is responsible for coordinating movement.
- Tegmentum: This is an evolutionary part of the brain. It forms part of the reticular formation – a set of nuclei that are responsible for arousal and attentiveness. They can be found throughout the brainstem.
The medulla (in yellow) is located on the brain stem between the pons and the spinal cord. It serves as a passage for ascending and descending nerves. Think of it as the highway of nerves. The medulla houses the control center of important body functions like breathing, blood pressure, and heart rate. It is also the reflex center for sneezing, coughing, and vomiting. The medulla is an essential part of daily functioning, hence damage to the medulla could lead to loss of sensation, impaired reflexes, respiratory failure, or even paralysis.
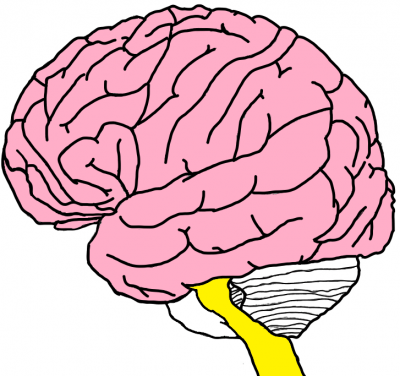
The Medulla contains the nuclei and several tracts that act as a passage for the ascending and descending nerves.
- Nuclei: This is a cluster of neuronal cell bodies within the central nervous system (CNS).
- Tracts: A tract is a bundle of axons, usually myelinated, that connects the nuclei of different parts of the CNS.
Patel, Hamish, and Yuri Sugano. “The Pons.” TeachMeAnatomy, 6 Dec. 2020, teachmeanatomy.info/neuroanatomy/brainstem/pons.
Vaskovic, Jana. Medulla Oblongata, Kenhub, 3 June 2021, www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/medulla-oblongata-gross-anatomy.
*This site content is provided for informational purposes only and does not intend to substitute professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you have medical questions and/or concerns, please contact a medical professional.