The brain is a complex structure that has many parts. Of course, this is to be expected, especially since it is the coordinator of the body. The main parts of the brain are the cerebrum, cerebellum and the medulla. There are other structures that are not as prominent as the three mentioned above.
The cerebrum, which is the largest brain structure, has four lobes that are very important to our existence as humans. The frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal lobes all have different functions and damage to any or all could be fatal to the individual. Other structures that will be discussed are the medulla and the pons. More information on the frontal lobe can be found as you scroll through this page.
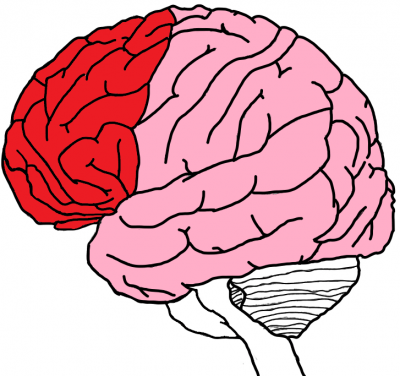
The frontal lobe (in red) is located anterior (that is to say, in front of) to the temporal and parietal lobes, just behind the forehead. It interacts with the limbic system in order to regulate emotions and behavior by releasing biochemicals. Having a strong role in cognitive functions, the frontal lobe is responsible for:
- Coordinating voluntary movements — walking and picking up objects.
- Impulse control — assessing the consequences of actions.
- Language comprehension
- Formation of long-term memories
- Emotional expression
- Development of personality
- Management of the reward system
- Regulation of attention
- Medial frontal lobe: This contains structures like the cingulate gyrus, which is a part of the limbic system, and the frontal gyrus which plays a role in self-awareness.
- Lateral frontal lobe: This contains the superior frontal gyrus which also plays a role in self-awareness. Additionally, it contains the middle frontal and the inferior frontal gyrus. The inferior frontal gyrus plays a role in language processing.
- Polar region: This contains the frontomarginal gyrus and the transverse frontopolar gyri.
- Orbital frontal lobe: The orbital frontal lobe contains numerous structures including the anterior orbital gyrus, medial orbital gyrus, posterior orbital gyrus and gyrus rectus. The orbital gyrus is a part of the limbic system and it is responsible for coordinating and controlling emotional and automatic reactions.
- Attention difficulties
- Declining intelligence
- Changes in emotion, anxiety or depression
- Difficulty understanding social cues
- Loss of memory
SpinalCord.com Team. Frontal Lobe: Function, Location, and Structure, 4 Nov. 2020, www.spinalcord.com/frontal-lobe.
*This site content is provided for informational purposes only and does not intend to substitute professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you have medical questions and/or concerns, please contact a medical professional.